In the world of digital marketing, we live and die by web services and platforms for every aspect of our work. For new SEOs, the sheer wealth of new tools can be overwhelming, to say the least. You have:
- SEMRush, Ahrefs and more for Organic Research
- Google Analytics and Google Data Studio for Analysis and Reporting
- Screaming Frog and a combination of Chrome Extensions and your browser for TSEO
- An entirely new vocabulary of SEO jargon and acronyms to learn
If you’re thinking to yourself, “I have no idea what he is talking about” - take a step back and check out our Essential Starter Kit for New SEOs - then return to this post.
Google Search Console
If you are familiar with those tools, then you’ve likely dabbled in Google Search Console at some point in your SEO journey. Search Console is a versatile tool that provides webmasters with a plethora of data to use for every aspect of digital marketing.
For Search Engine Optimization, in particular, GSC can be broken down into two main sections:
- Performance (search performance data)
- Index (TSEO specs like coverage, sitemaps and removals)
While Google Search Console can be utilized for all things SEO, we could go on for days discussing every aspect of the tool. For the sake of practicality, this post will serve as a beginner’s guide to the Google Search Console Performance section. More specifically, shedding light on the often dark and confusing abyss of GSC metrics.
Impressions, Clicks and Position: What’s the Difference?
When first introduced to Google Analytics or Google Search Console, a difficult concept to grasp is the difference between metrics and dimensions. Simply put, metrics refer to numerical, quantitative search data.
In Google Search Console, there are four core metrics:
- Impressions
- Clicks
- Position
- Click-Through Rate
If you’ve worked in GSC for SEO before, these terms are likely familiar. However, not all SEOs (especially those new to the industry) have a clear and concise understanding of each metric. For a complete breakdown of these metrics in GSC, check out the Google Webmasters support document. We’ll be highlighting the top concepts to note from that document. So, strap on your goggles and scuba gear as we dive headfirst into the hazy waters of Google Search Console’s performance metrics.
Note: Here at Seer, we calculate our own CTR using multiple data sources and PowerBI - so we won’t touch on GSC Click-Through Rate in this post.
What Exactly is an Impression in Google Search Console?
Google defines impressions in Search Console as “how many links to your site a user saw on Google Search results”. While that serves as an adequate definition for directional purposes, it can be misleading if you take it at face value.
A more accurate definition of Google Search Console’s impression metric is the number of times a user loads a page on Google where your site ranks in any position. Did you read that clearly? Any position. An impression is recorded as long as your result is on the page that’s loaded, regardless of whether it’s been scrolled into view.
What exactly does that mean? It means results below the fold, never seen by the human eye, are counted as impressions. If you’ve been using GSC impressions to measure your organic reach, you may want to think again.
Picture this:
You’re waiting in a room with nine (or more) other strangers, all trying to impress one person (let’s call them, the Bachelor). However, you weren’t strategic in how you optimized your position and now you find yourself located directly behind the door. When it swings open, you’re blocked from view and before you have the chance to move, the Bachelor walks out of the room and slams the door shut - without ever laying eyes on you. Would you consider that a strong first impression? Or any impression at all?
Well in organic search:
- You’re a search result tucked away at Position 10
- The Bachelor is a user equipped with a credit card and eager to find the best solution to their pain point, and;
- Google considers that non-existent encounter an impression.
I don’t know about you, but I’d say your chances of receiving a coveted organic rose are slim-to-none in that case.
 Bottom line: impressions are not an accurate representation of how many users physically view your search result.
Bottom line: impressions are not an accurate representation of how many users physically view your search result.
What Determines a Click in Google Search Console?
When you press your finger on the mouse, you consider that a click, right? Google has different thoughts when it comes to Search Console. A click in Google Search Console is only registered when the user physically leaves the SERP.
Two exceptions to this are:
- If a user clicks to a link outside of Google, returns to the SERP, and clicks on that same result again (a.k.a. pogo-sticking) - that counts as one single click in GSC, even though they left the SERP twice.
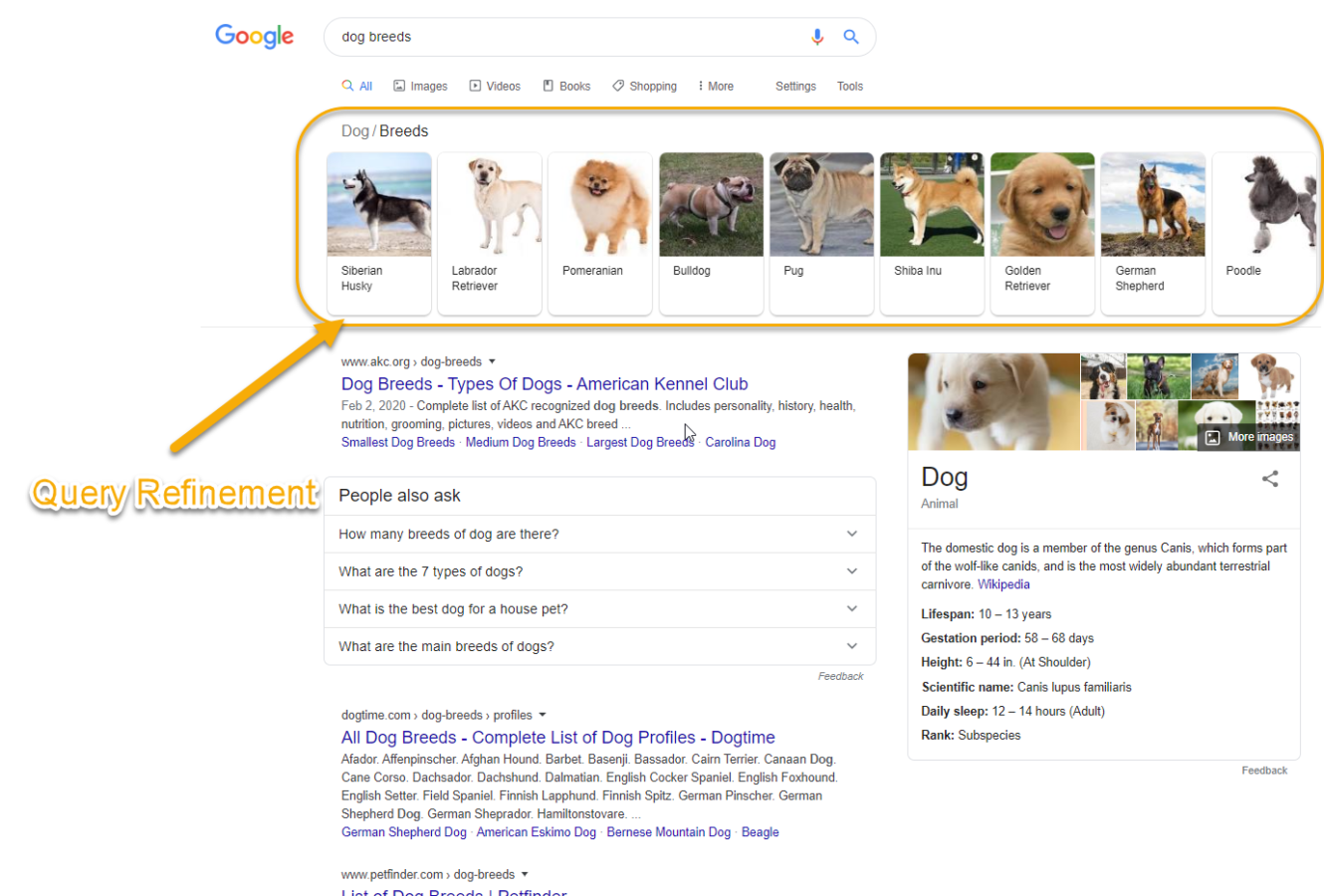
- Clicking on query-refinements, such as a carousel that points to a new search, is not counted as a click.
 The term ‘dog breeds’ triggers a query-refinement carousel for specific breeds. Although all of these good pups deserve an organic search milk-bone, clicking on any of the specific breeds will refine the SERP to results for that one breed and Google Search Console will not count that as a click.
The term ‘dog breeds’ triggers a query-refinement carousel for specific breeds. Although all of these good pups deserve an organic search milk-bone, clicking on any of the specific breeds will refine the SERP to results for that one breed and Google Search Console will not count that as a click.
What is Position in Google Search Console?
Have you ever wanted to get a close-to-exact gauge on where you’re ranking on Google? I’m here to tell you that Search Console is NOT the place for that! On the surface, Position sounds rather straightforward - your position in the SERP. Think again.
Position value in Google Search Console is the average position for all searches. Search Console labels the metric ‘Average Position’ on the Performance graph, but it is displayed simply as ‘Position’ in the Performance table.
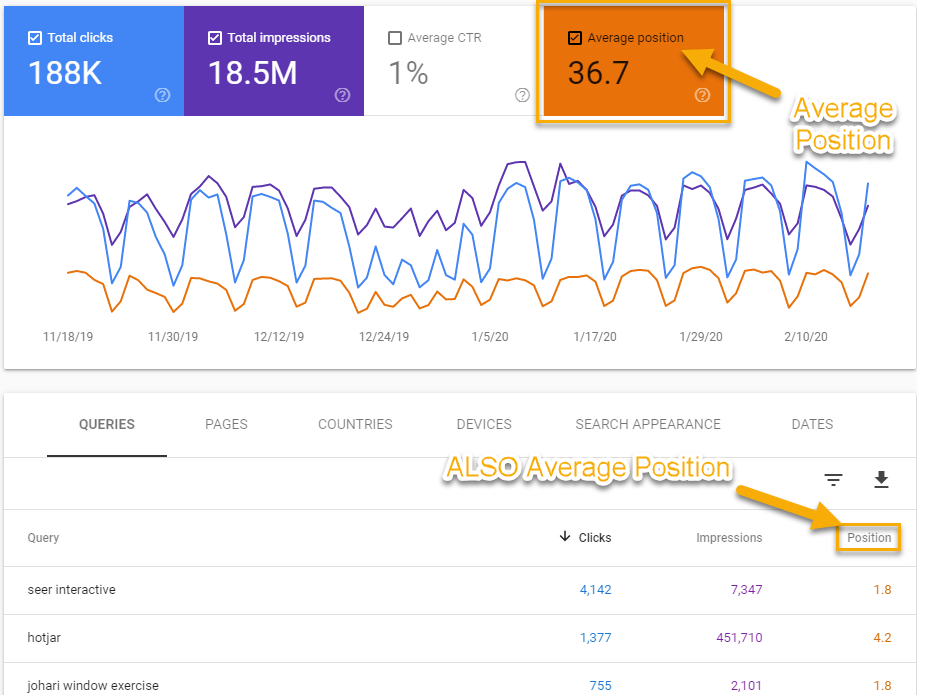
So place the emphasis on average, because GSC calculates the average position which can vary for a number of reasons including, but not limited to:
- Search history
- Location
- Personal Preferences
Now you know that Google Search Console displays Average Position, but how is it calculated?
How Does Google Search Console Calculate Average Position?
Google is a hotbed for complex calculations and algorithms, so it comes as no surprise that Average Position isn’t simply the average position of all searches for one URL. Let’s take a look at the factors that go into calculating average position.
GSC Only Counts the Topmost Link
If multiple pages to your site are displayed on the same SERP for a query, Google takes the topmost link to your domain in the search results averaged across all queries where it appeared.
If the gears in your head are spinning, don’t worry - we have an example!
- For a particular query, you have three separate URLs ranking on Page 1 in Position 1, 3 and 5; GSC counts that as Position 1
- A separate query displays those same three URLs on Page 1, but this time in Position 6, 8 and 9; GSC counts that as Position 6
- Google Search Console would calculate that as an Average Position of 3.5
- [(Position 1 + Position 6) / 2 (total # of queries)] = 3.5 (Average Position)
Location Matters for Average Position
In General, owning a knowledge panel on the side of the SERP is a better spot than Position 10 at the bottom of the page. In GSC, that’s not the case.
Google Search Console awards position left-to-right then primary-to-secondary (left-to-right in English, though it varies depending on the language). So even though most featured snippets would be in Position 1, that knowledge panel on the right-hand side would be ranked after the last blue-link result on Page 1.
One important note: Google Ads do not count for position. If a query triggers four PPC ads and the fifth result is below the fold, users have to scroll to view ‘Position 1’ in GSC.
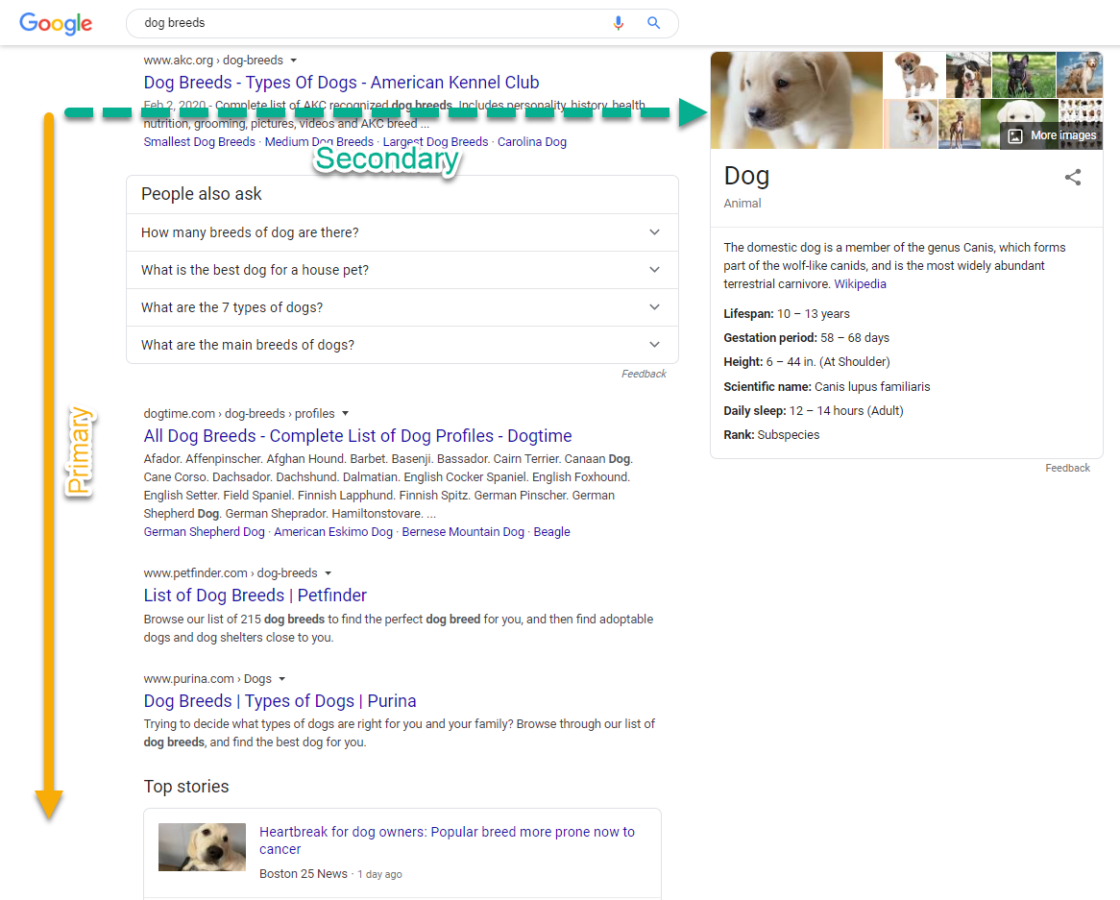
 Using ‘dog breeds’ once more: though the knowledge panel with the adorable pup catches the eye of most users, Google Search Console would credit that with the LAST ranking on Page 1 despite being above the fold.
Using ‘dog breeds’ once more: though the knowledge panel with the adorable pup catches the eye of most users, Google Search Console would credit that with the LAST ranking on Page 1 despite being above the fold.
Caveats for SERP Features and Elements in GSC
Now that we’ve cleared up exactly what impressions, clicks and average position is in Google Search Console, let’s take a look at some exceptions when it comes to SERP Features and Elements. SERP features that have multiple URLs, like carousels and knowledge panels, have special exceptions with regard to their metrics in GSC.
Carousels Must Be Scrolled Into View for Impressions
Unlike standard results, listings that trigger carousel results must be scrolled into view. For example, if a query triggers a news carousel in Position 9 and the user doesn’t scroll below the fold, GSC does not count that as an impression for any of the links.
All Links within a SERP Element Receive the Same Average Position
Whether it’s an answer box from one source or a carousel of more than ten sources, each URL will have the same average position in Google Search Console. For example: if a news carousel is triggered at Position 2, all URLs in that carousel are considered to be in Position 2.
Multiple Links Leading to the Same URL Receive a Single Impression
If there are multiple links leading in a SERP element that lead to the same exact URL, all links to that site will be counted as one, single impression. However, if the links lead to different URLs on the same site, each URL will receive separate impressions.
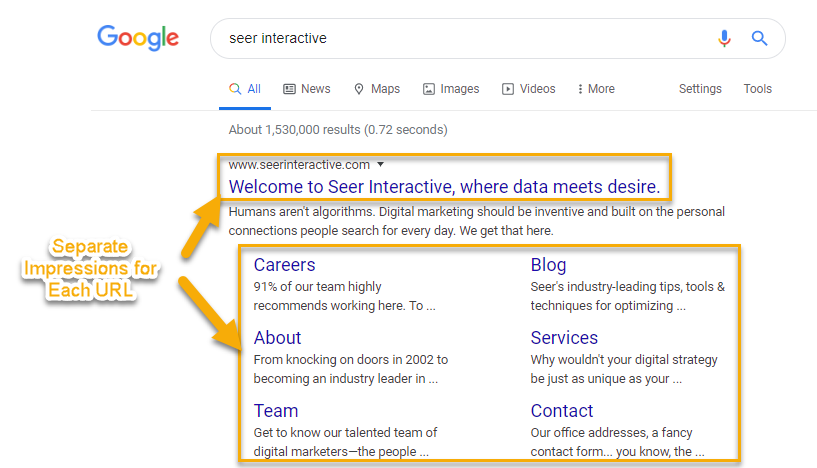
Rich Results
There is an additional caveat that’s specific to Rich Results, such as Job Postings and Events. Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to highlight that Rich Results are displayed in two different views:
- List View
- Details View
Let’s take a look at how Google Search Console treats each of these views.
List View
For Rich Results like Jobs and Events, the initial shortlist served in the SERP is referred to as list view. Metrics for list view are determined in a different way that other SERP features.
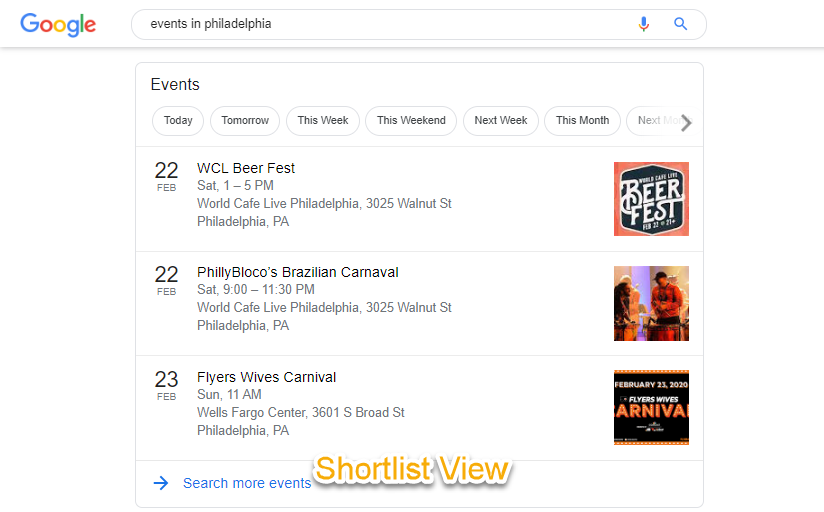
Impressions: There are multiple factors that weigh impressions for list view results. Impressions are counted in list view when:
- A list item is visible in the shortlist view on the original SERP page
- Ex. The top three events in the ‘events in Philadelphia’ shortlist would get impressions
- When the list view is expanded, whether or not the URL is actually scrolled into view (Note: Results that are visible in both short and expanded list view receive two impressions)
- Ex. Clicking the ‘search more events’ link would expand the list view and all items on the list would receive impressions
Clicks: Clicking a specific item in list view counts for that URL only.
Position: There are multiple factors that determine Position in list view results, including:
- All visible results are assigned the same position in shortlist view, wherever the feature is positioned on the SERP
- Each item is assigned separate positions within the expanded list view
- Ex. If a list rich snippet is in Position 1 on the SERP: a result in Position 2 of the shortlist is assigned Position 1 for the shortlist view and Position 2 for expanded list view, for an Average Position of 1.5
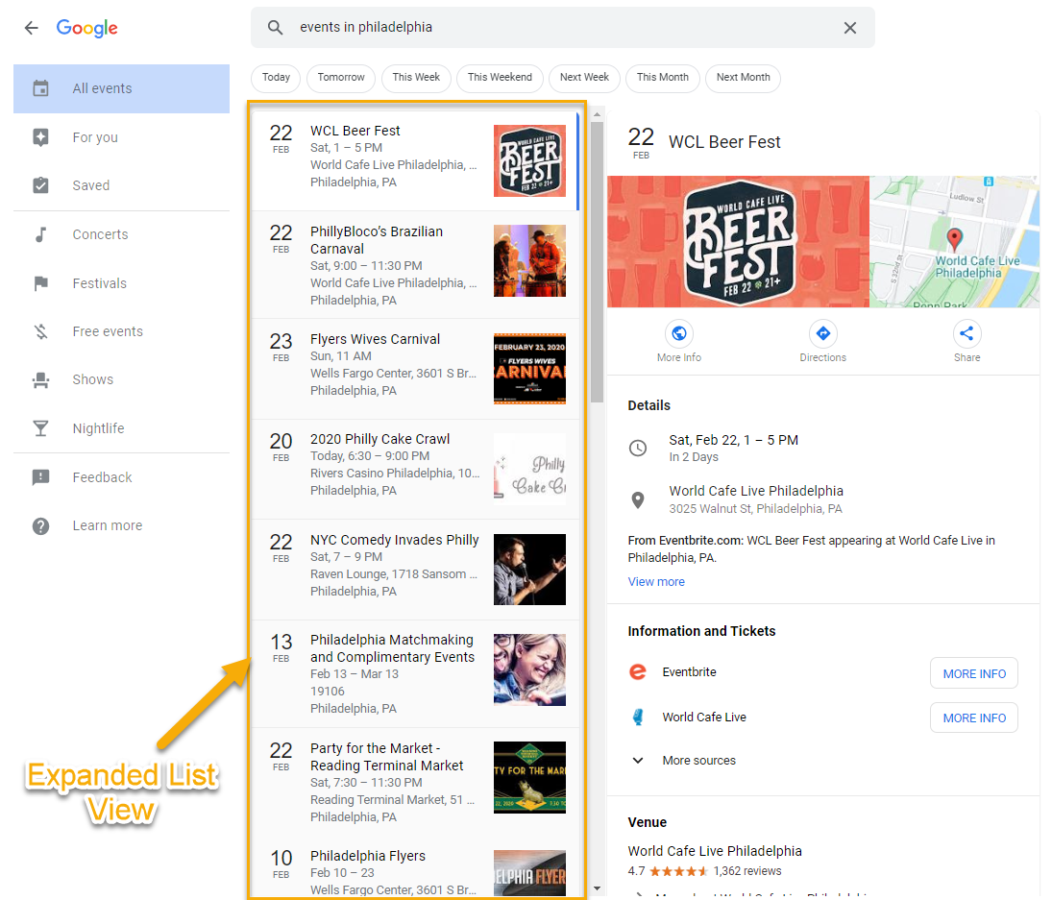
 Since the event shortlist result is in Position 1 of the SERP, the PhillyBloco’s Brazillian Carnival event would have an Average Position of 1.5 (Position 1 on the shortlist and Position 2 on the expanded list)
Since the event shortlist result is in Position 1 of the SERP, the PhillyBloco’s Brazillian Carnival event would have an Average Position of 1.5 (Position 1 on the shortlist and Position 2 on the expanded list)
Details View
When users click on a result in list view for Rich Results, Google opens to the details view. It’s important to note that details view can be opened in one of two ways:
- Clicking a result in list view
- Following a direct link to the details view (if someone shares the link to details view directly)
Metrics for details view are determined separately from those in list view.
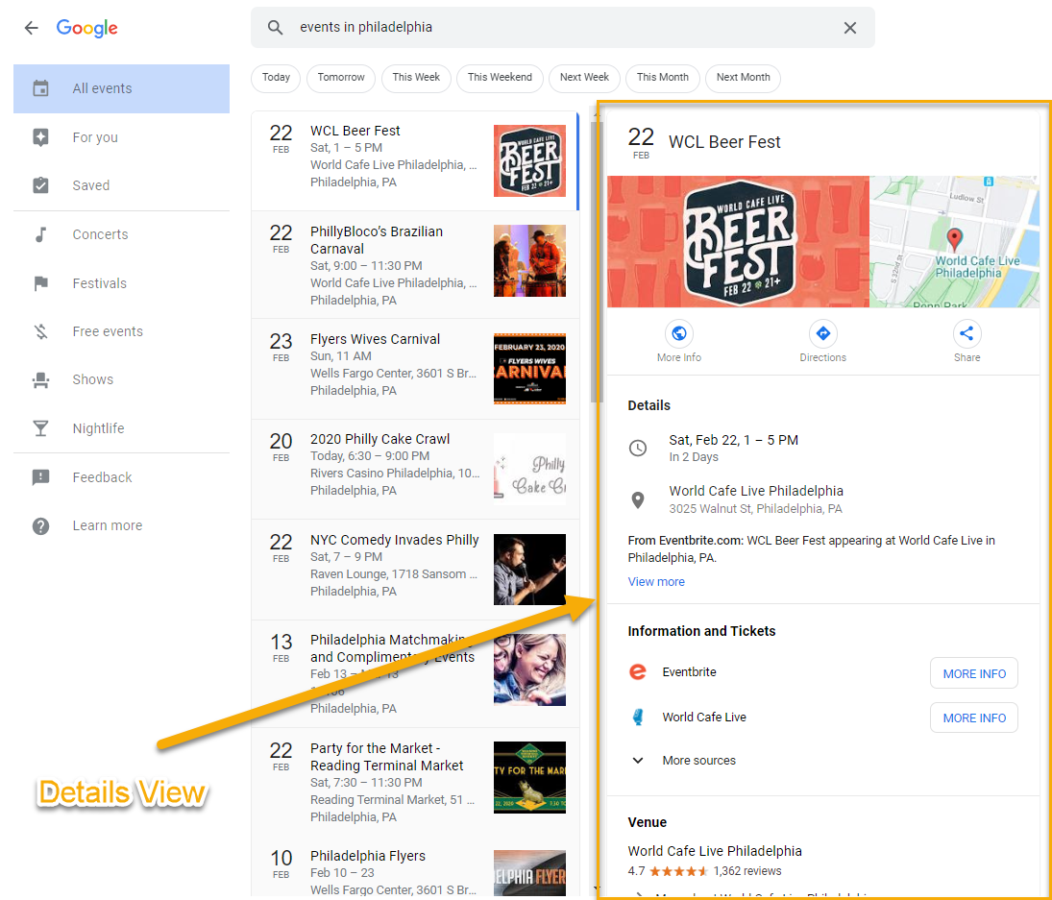
Impressions: All URLs shown in details view receive an impression
- Ex. Both ‘more info’ links in the result above receive an impression
Clicks: Clicking on a result in detail view counts as a click for the URL selected. When a details view displays multiple URLs, only one URL can receive a click.
Position: In details view, the result is always Position 1.
Impressions vs. Clicks in Details View
Remember how there are two ways to trigger details view? This can cause impressions to be higher than clicks for several reasons, including:
- When someone opens a direct link to the details view that has been shared with them, GSC counts one impression for details view but zero impressions or clicks for list view
- On desktops, clicking the link to expand list view automatically displays the details view for the first result - which counts as an impression without a click
Google Search Console for Discover: Mobile Specifics
Google Search Console added a tab for Discover data in the Performance section in 2019. With mobile searches consistently increasing, this data can be useful in gauging mobile performance in GSC. Let’s take a look at how mobile-specific metrics are determined for Discover.
- Impressions are only counted when a Discover card comes into view, and only one impression is counted per result.
- Clicks are only counted when a user physically clicks the card
- Position is not determined
Image Results in Google Search Console’s Performance Section
When it comes to image results, there are two different views in Google:
- Combined SERPS where images are embedded alongside standard SERP results
- Image SERPs which serve images exclusively
If there are multiple images on the same URL, Google Search Console counts all of the images as one. This means that impressions, clicks and position for different images are assigned to the same URL. However, if the same image appears in both combined SERP results and image SERP results, GSC will record the data for each result separately.
Let’s take a closer look at how Impressions, Clicks and Position are assigned as it relates to images in combined SERPs and image SERPs.
How are Impressions Assigned for Image Results in GSC
Impressions are only counted once for image results, so if a user scrolls past and then returns, it’s only counted as a single impression. When an impression is actually recorded depends on which SERP view is served.
- Combined SERPs count impressions whether or not the image has been scrolled into view in the browser, similar to standard results. One exception: Images inside of a carousel must be scrolled into view in order to receive an impression.
- Image SERPs only count impressions when the image is physically scrolled into view.
How are Clicks Counted for Image Results in Search Console?
This one is pretty straight forward: clicking on an expanded image, or any image click that takes the user out of Google’s SERP is counted as a click. Much like standard results, expanding a thumbnail image within Google does not count as a click.
GSC keeps it simple for image clicks!
How is Position Determined for Image Results in Google Search Console?
Position, as it relates to images, is determined based on the SERP view they are served in.
- Combined SERPs calculate position using the standard rules, where a block of images all receive the same position within the SERP.
- Image SERPs are a tad different. Results are counted left-to-right then top-to-bottom, similar to a snake draft for those of you fantasy sports fanatics.
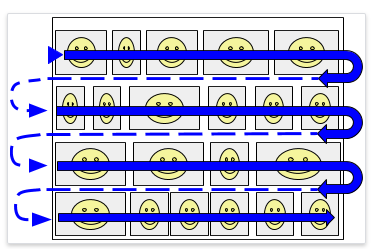
For image SERP results, screen size comes into play as it varies by device. Wider screens will show more results per row, so it’s very difficult to understand position value for image SERP results in GSC.
Google Search Console Performance Data for SEOs
So we’ve cracked the code on impressions, clicks and average position in Google Search Console. With a clear understanding of the data at hand, Search Console can be a powerful tool with many capabilities. It is extremely important to understand how to utilize GSC in your work as an SEO.
When Should an SEO Use GSC Performance Data?
Directionally. If there’s anything that you’ve learned by reading this guide, it’s that a significant amount of variables, calculations and caveats go into determining Google Search Console metrics. For that reason, SEOs should only use GSC Performance Data for directional purposes.
A few opportunities to leverage Google Search Console Performance Data for SEO include:
- Diagnosing a decline in organic traffic to your site
- Surfing through GSC’s search term data as an additional Keyword Research tool
- Combining GSC data with other data sources in PowerBI to calculate your own Click-Through Rate
- Calculating estimated ROI with that custom CTR you’ve created in PowerBI
Are There Any Ways I Shouldn’t Use Search Console Performance Data?
Glad you asked, YES! In contrast to directionally using GSC data, all of those variables that go into the metrics make the data shaky (at best) for definitive reporting.
Google Search Console Performance Data should not be used in SEO in the following ways:
- Using average position to report keyword rankings in Google to your client (never)
- Using impressions to report on traffic and visibility in Google to your client
- Reporting organic performance in any significant client-facing meeting as a way to communicate the value of SEO to executives
Dive Into Google Search Console Performance Data
Now that you have a better understanding of Performance Data in Google Search Console, it’s time to dive in and start leveraging a useful resource! If you’re still feeling shaky about Google Search Console, or want to learn more about all facets of SEO, PPC, Analytics and Digital Marketing, sign up for the Seer Interactive newsletter in the form below!