What Is a Canonical URL?
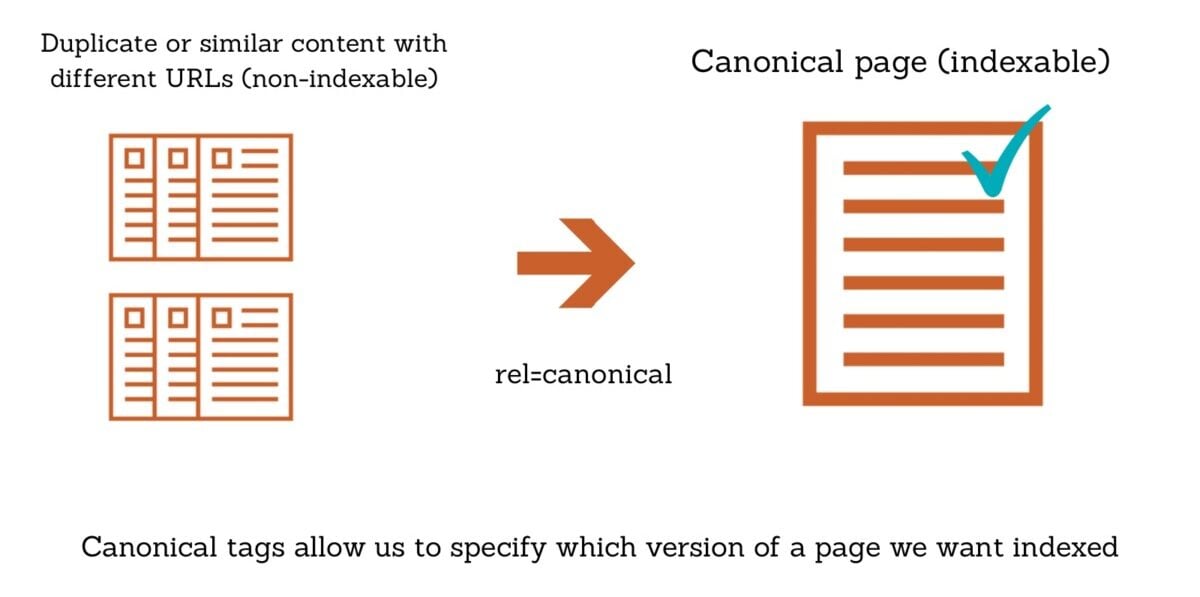
First implemented by Google in 2009, canonical URLs and tags are a technical solution used by webmasters to help search engines identify the original or master copy of a web page.
By utilizing a canonical tag, webmasters can prevent duplicate content issues by indicating to search engines their preferred or “canonical” version of a web page.
In this blog post, we will cover:
- What Are Canonical Tags and URLs?
- How to Specify Canonical URLs
- Why Are Canonical Tags Helpful for SEO?
- Best Practices for Canonicalization
What Are Canonical Tags and URLs?
The most common way to specify a canonical URL is through the use of a canonical tag. Also known as “rel canonical”, the canonical tag is an HTML tag placed in the <head> section of a page that indicates to search engines the preferred URL of a web page. Canonical tags will look like this:
<link rel=”canonical”, href=”https://www.preferredurl.com”>
Example:

The enclosed url within the href attribute is known as the canonical URL.
Self-Referential Canonical Tags
Canonical tags can also be used to reference a page back to itself. This is known as a self-referential canonical tag. While not mandatory, Google recommends using self-referential canonical tags to be explicitly clear which URL should be indexed.
Since Google views even differences in trailing slashes for the same page as different URLs, utilizing self-referential canonical tags can ensure Google is aware of your preferences.
How to Specify Canonical URLs
Canonical URLs can be set up in a variety of ways in addition to the canonical tag method mentioned above. Some methods Google provides are:
- Send a rel=canonical header in your page response
- Specifying canonical pages in your sitemap
- Utilizing 301 redirects
Please note that Google does not explicitly require webmasters to utilize canonical tags. Google can identify what they interpret to be the best version of a page or URL on their own based on a variety of page signals.
You can use the URL inspection tool found within Google Search Console to identify which URL Google considers canonical.
Why Are Canonical Tags Helpful for SEO?
Multiple URLs for the same page are quite common as a result of a site supporting multiple device types or dynamic URLs. As a result, canonical tags can be incredibly useful for SEO purposes including, but not limited to:
- Specifying which URL you want people to see in search results
- For example, if you would like for visitors to visit a specific product page through https://www.uniqlo.com/us/en/men-ultra-light-down-jacket-443318.html rather than the same product page with a slight variation, such as color: https://www.uniqlo.com/us/en/men-ultra-light-down-jacket-443318.html?dwvar_443318_color=COL46.
- Consolidating link signals for similar or duplicate pages
- You can help search engines consolidate information they have from multiple URLs into a single, preferred URL. Therefore, https://www.uniqlo.com/us/en/men-ultra-light-down-jacket-443318.html?dwvar_443318_color=COL46 can have its link signals consolidated towards the main product page https://www.uniqlo.com/us/en/men-ultra-light-down-jacket-443318.html
- Simplifying tracking metrics for a single product or topic
- You can consolidate metrics for a single web page through the use of canonical tags.
- Managing syndicated content
- If you share syndicated content on other domains, you can ensure that your preferred URL appears in SERPs with canonical tags.
- Limiting crawl time on duplicate pages
- You can help ensure Google crawls new or updated versions of pages rather than crawling two versions of the same page through the use of canonical tags.
Best Practices for Canonicalization
Google provides general guidelines for canonicalization:
- Use the absolute, lowercase URL of a page rather than the relative path when specifying a canonical URL
- For example, you will want to use the entire URL “https://www.preferredurl.com/green_dress_1” over “/green_dress_1” when specifying a page.
- Do not use the robots.txt file to canonicalize pages.
- Do not use the URL remove tool for canonicalization. The URL removal tool will remove all versions of a URL from search.
- Do not canonicalize two different URLs that point to the same page using different methods.
- For example, do not specify one URL using a sitemap and then also apply a rel=”canonical” on the same page and specify a different URL from the one specified on the sitemap.
- Do not use noindex tags to prevent Google from canonicalizing a page. This tag is meant to exclude a page from the index, rather than used to manage canonical pages.
- Canonical pages should be specified when using hreflang tags. As Google recommends it -- “specifying a canonical page in the same language, or the best possible substitute language if a canonical page does not exist for the same language.”
- When internally linking, use the canonical URL when possible. Linking consistently to the canonical URL helps Google identify your preferences.
- Utilize HTTPS over HTTP when possible, as Google prefers the HTTPS domain protocol over the HTTP domain protocol for canonical URLs.
How Should You Use Canonical Tags?
Canonicalization is an incredibly useful tool to help make it easier for Google and other search engines to evaluate your content and its quality. Ultimately, canonical tags allow you to indicate to Google the specific URL/page you want indexed, thereby helping prevent any potential duplicate content issues.
Since setting up canonicals varies on your content management system, contact your website administrator first to learn more about how to set up canonicals on your site.



