This is the first post of a series where I'm going to cover the different phases of an International SEO process, from researching and establishing your International SEO strategy and goals to measuring the advancement and results over time:
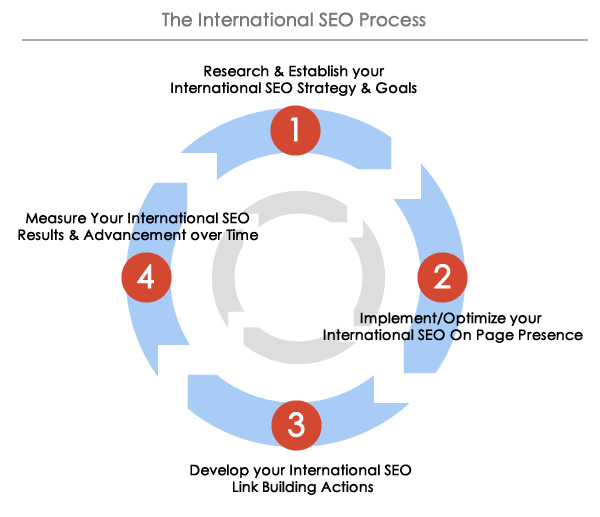
Let's start with the first phase of the International SEO process:

1. The Importance of an International SEO Strategy & Goals
Although during the first SEER International SEO Q+A most of the questions we had about International SEO were about specific tactics or implementation doubts, these are usually the result of an International SEO strategy that hasn't been well established at the beginning.
Unfortunately some of the most common issues with international Websites happen because they're implemented and optimized without real planning and research, just by extrapolating the content and structure of the main site version without taking into consideration that each of the languages or countries targeted have a specific audience, competition and industry behavior:
- The top products or services for other languages or countries won't necessarily be the same than the ones of your main language or country version.
- The products or services in other languages or countries won't be searched necessarily with the exact same "translated" phrases or terms.
- The sector or industry seasonality might be different in each country or language, with specific cultural or geographic influenced festivities.
- The competitors in different countries or languages won't necessarily be the same, neither their unique selling proposition nor the offering that you will need to compete with.
- The search volume and potential organic traffic in other languages or countries will be different.
- There might be local search engines in some countries that are more important that Google and you will need to optimize and rank for them to be where your audience is (for example, in Russia is Yandex and in China is Baidu).
Therefore, when you develop and start optimizing for other languages or countries you cannot simply extrapolate what you already have in your current site. Of course, this will be used as an input but you cannot obviate the specific characteristics of each one of the countries and language audiences that you will target: You need to take them into consideration to establish an effective Web presence and SEO strategy.
2. Identifying your Online International Opportunities
The first step to set your international SEO strategy is to identify your online business opportunities based on:
2.1. Your online business model and operations
How does your online business work? What's your online business model? What's your online business goal? Is it completely based on your site or do you provide local services or products? How do you deliver them? Do you have the capacity to provide them in any country and in any language? Which are the existent restrictions and how high would be the additional costs?
Unfortunately is not always feasible or beneficial to deliver your products or provide your services in any country. Maybe you sell some type of food and you need complex permissions to obtain. Or you can send your small products worldwide but there are important delivery costs and timings that you need to take into consideration.
Make sure to identify the implications of going international from the start, otherwise you might end-up wasting your time and resources afterwards since you will discover too late that there's no way your sales are going to be as high to compensate the needed International investment.
2.2. Your current visitors demographics and behavior
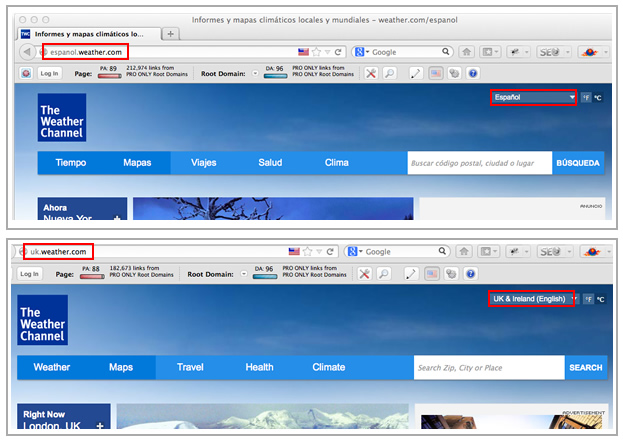
Verify the language and countries of your current audience with your Web analytics systems. If you use Google Analytics you can go to the "Audience > Demographics" reports and check which are your current visitors languages and locations:
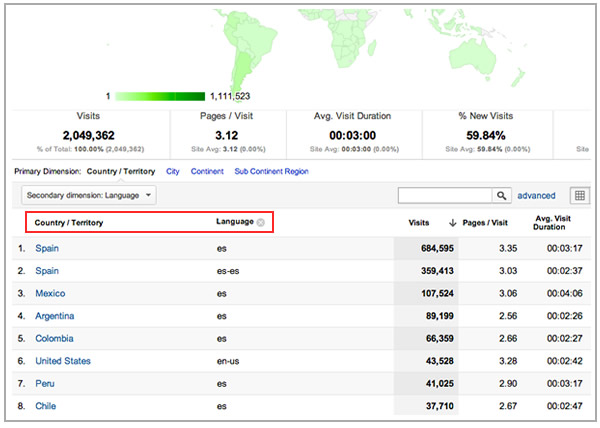 Once you identify the most important languages and countries you can start digging deeper to discover the behavior of these visitors:
Once you identify the most important languages and countries you can start digging deeper to discover the behavior of these visitors:
- Which keywords they used and which pages they visited?
- Which services or products they ended-up buying?
- How high is the conversion volume and their conversion rate compared to your main country or language?
Apply an organic traffic segment and specifically identify this information for it to compare.
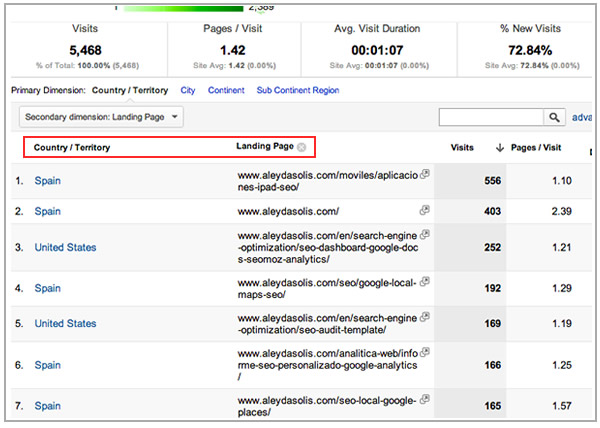
Finally, remember to check the general and organic traffic sources per language and country. Which are the most important search engines and sites, in general, referring you traffic per country and language?
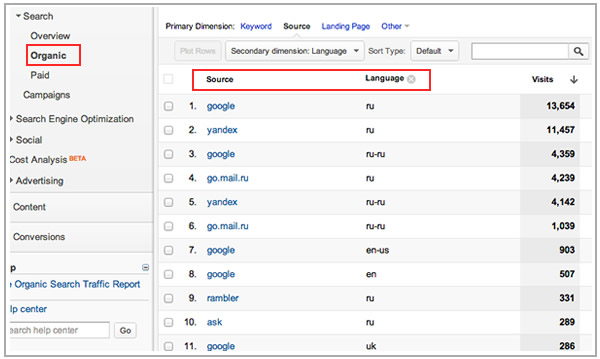
Once you've internally analyzed your present traffic volume, behavior and conversions from other countries and languages you will have a much better vision about which are those that you should take into consideration and further research their market potential.
2.3. Your industry international potential
The next step is to start the research for potential organic traffic volume, its behavior, keywords and competitors in these international markets so at this point if you don't speak the language it's important to have a local native to support you with this activity. Don't worry, it shouldn't be that complicated if you keep some good practices I shared in this article into consideration.
Start always by validating with services such as Alexa’s top sites per country and StatCounter which are the most popular search engines in those countries you've already identified as potential markets for your international expansion.
If Google is not the main local player keep in mind that you will need to research which are the most important ranking factors in these other search engines and develop your local search market research with them. Local search engines will offer an alternative to do keyword research, for example, you have Baidu Index for China and Yandex Keywords Stats for Russia and CIS Countries.
In the case it's Google, you can start with its Keywords Tool by selecting the appropriate location and language and begin the research with the main keywords that you have already identified from those countries and languages in Google Analytics:
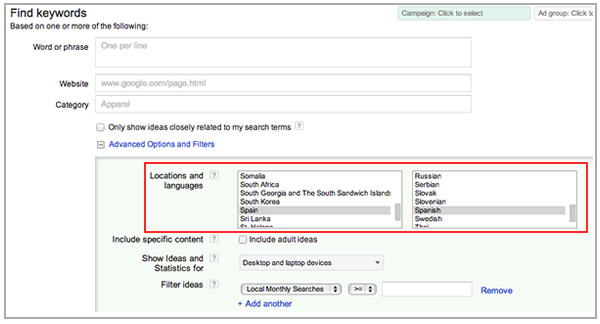
With these keywords suggestions, especially those for keywords with high search volume you can use tools such as Ubersuggest that also supports other languages to identify more keywords opportunities.
Additionally, to obtain more information about each keyword per country, you can use SEMrush and Search Metrics Essentials:
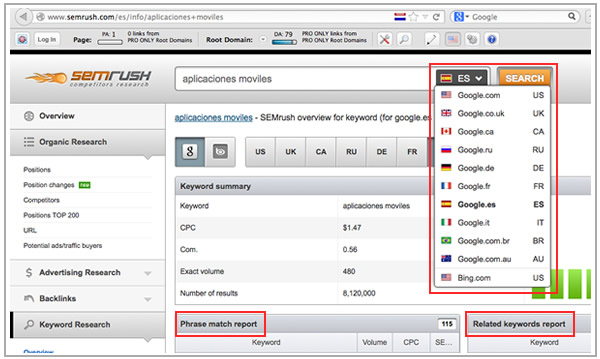
Using these same tools It's also important to verify which sites are already ranking for these keywords since they would become your competitors, check how they're structured, the type of content they're featuring, their link profile and social activity:
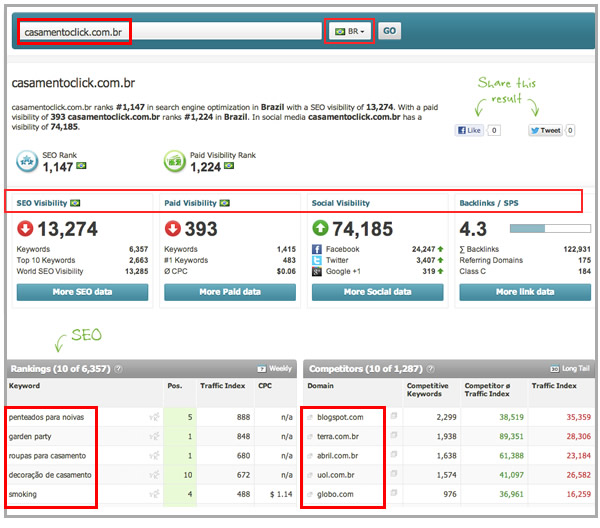
And with Google Trends verify the seasonality and behavior over time for the most important keywords per country, identifying which are the top and rising related terms for them:
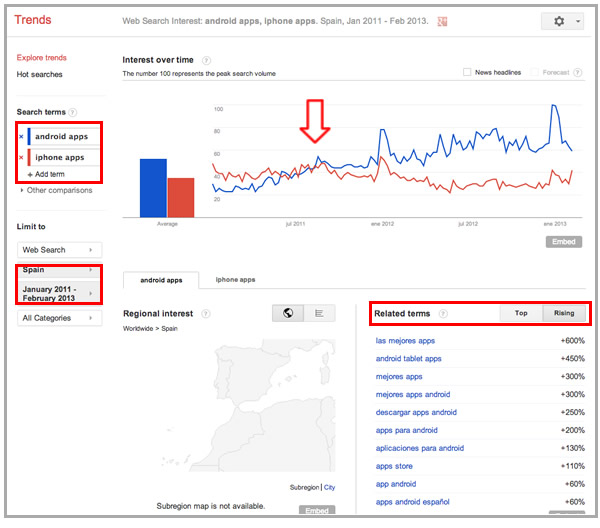
Google has also a tool called Global Market Finder, to help you identify international opportunities, but use it with care and better directly validate the suggested keywords as I described before, since as Andy Atkins pointed out in this post, it doesn't always work as you would expect.
2.4. Wrapping Up your International Analysis
By identifying your potential new languages and country markets, initially with internal information and then by researching each market information you will be able to validate if the countries and languages you had initially identified with potential from your current site activity really provide a high search volume and positive trend, with reasonable competition to make them attractive and potentially beneficial to target.
3. Setting the right International Targeting
The next step is to identify how you would target your international audience taking into consideration the information you've identified before in the research and in dependence on your online business characteristics and model: If it's better to target all the global audience speaking a specific language (no matter where they are) or specifically target a geographically focused audience, speaking a language (or a set of specific languages):
3.1. Language Targeting
A language targeted approach for your international presence is suitable when the location of the user is not a factor that influence the Website goals, content, service and product offerings.
This alternative will be suitable, for example, when you have identified in your analysis that you already attract visits that are highly distributed over many countries speaking the same language and in the research you have also verified the potential to attract new organic traffic and conversions is equally distributed with very similar terms, not specifically focused on one country.
This means that if you approach this situation with a specific version for each country you would end-up with a high amount of sites that won't compensate the effort and having many specific site versions won't have a high impact over the type of service or product you provide for these audiences.
A site can also start with a language targeted approach and evolve towards a country targeted one when it identifies it has enough activity from one specific country, with particular characteristics that will compensate to create a specific site targeting them with a unique product, service or content offering.
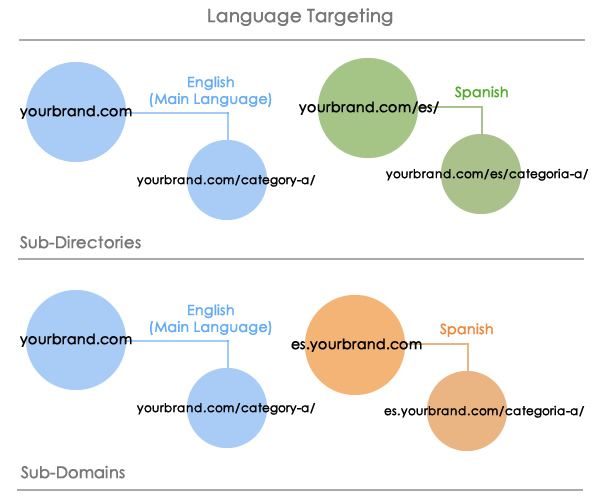
The website organization for a language targeted approach can be of sub-directories or sub-domains under the main generic top level domain, as it can be in the following graphic:
For example, Scribd and Shutterstock are both language targeted, but the first uses subdomains and the second uses subdirectories:
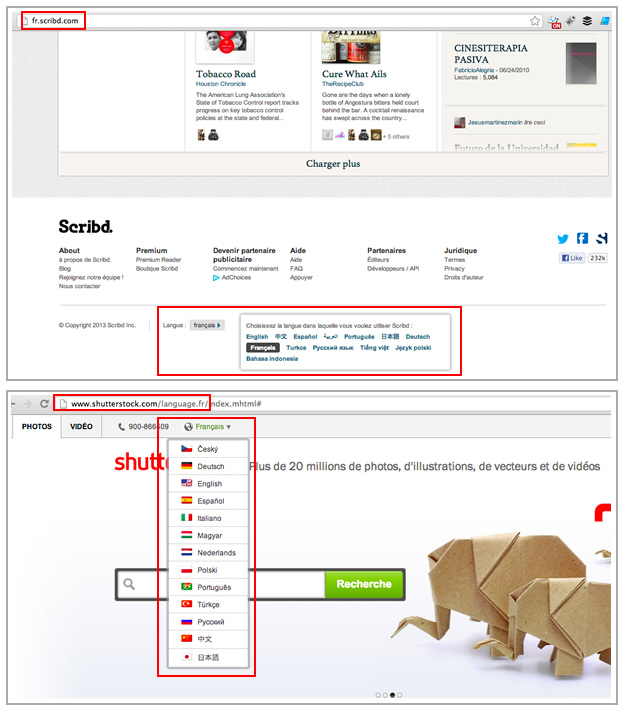
When you have a language targeted approach the best is not to feature a specific flag along the language, since you're really targeting all of the audience speaking the language that sometimes is not specifically located in one country and you might upset some of your visitors that won't be represented with the flag.
3.2. Country Targeting
A country targeted approach for your international presence is the best alternative when the location is a factor towards your online business model, goals and offering and you have enough country related search traffic potential to compensate the investment of building a site version targeting a specific country.
The website organization for a country targeted approach can be of ccTLDs (country code top-level domains), sub-directories or sub-domains depending on the main generic top-level domain, as it can be seen in the following graphic:
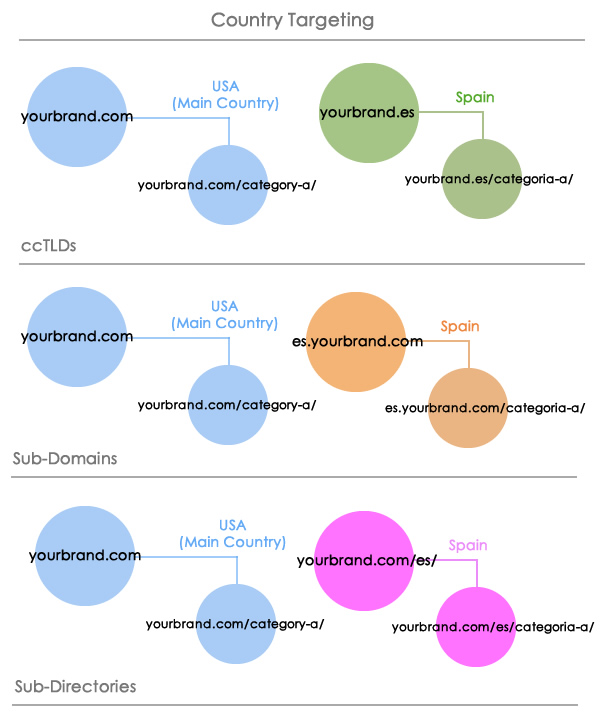
Additionally, you may reach a point in a mature market, where the audience in a specific country you're targeting speak many languages and you identify that you might be losing business opportunities with the audience based in specific regions where another local language is spoken.
In this situation you may want to run an additional research to identify the potential with this additional language and if it compensates create an additional language version with it, inside the same country site structure, that could be organized with any of the following alternatives:
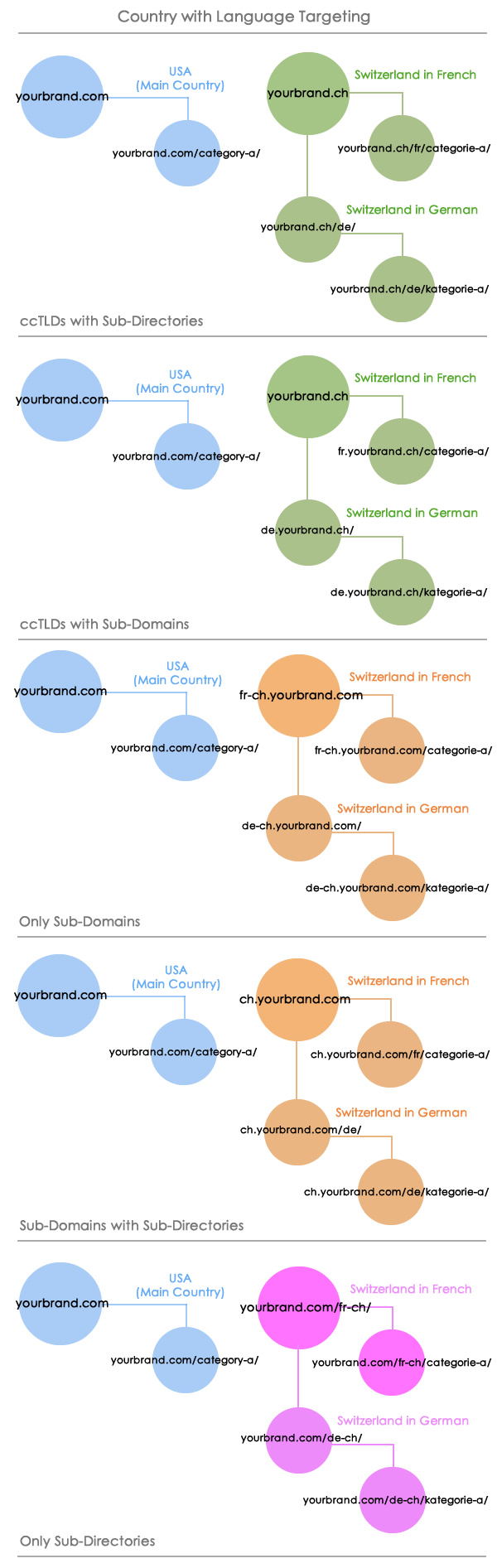
For example, Amazon is country targeted and uses ccTLDs. On the other hand, Microsoft is country targeted, with many additional languages for some of the countries and uses subdirectories:
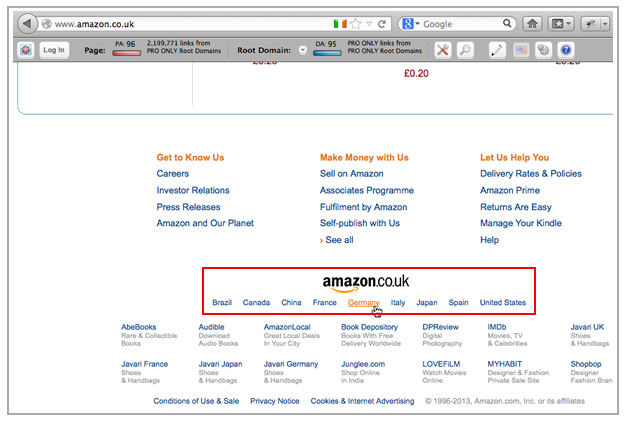
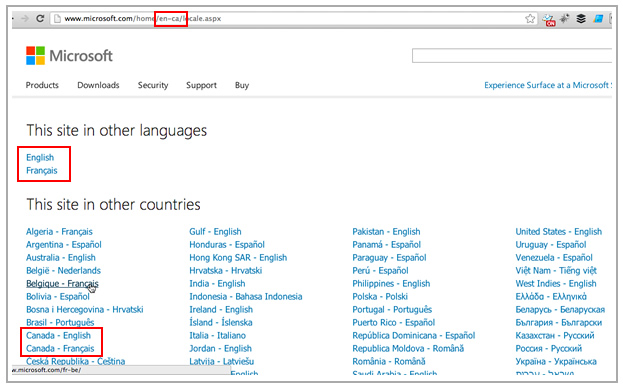
I will comment more about this in the next post of the International series --that will be focused on the execution of the International SEO process--, but since I know is one of the most frequent questions about this topic, I will advance a bit. From my experience the best approach to refer users from one country version to another --just in case they end-up in this situation (which should be a not so frequent situation if you correctly implement some geotargeting configuration through Google Webmaster Tools and Hreflang)-- is to friendly suggest the relevant version targeting their specific language or country, as Amazon does, and avoiding any automatic redirect based on the IP or browser language, that might be intrusive and sometimes complex to implement:
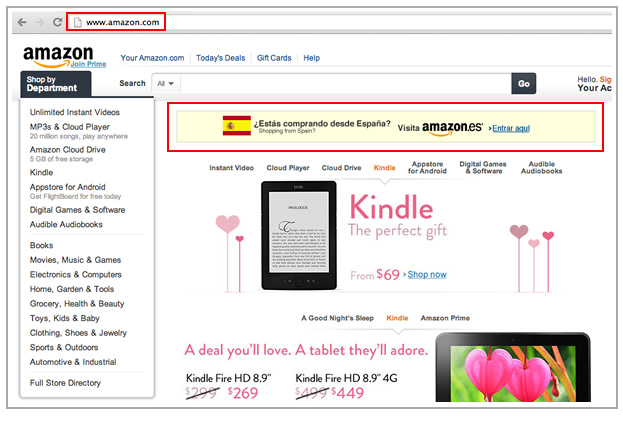
3.3. Wrapping Up International Targeting
All of the site organization alternatives --especially for the country targeted scenario, with ccTLDs, sub-directories and sub-domains--, have pros and cons as it can be seen in the following table I developed some time ago for this International SEO structure post at State of Search:
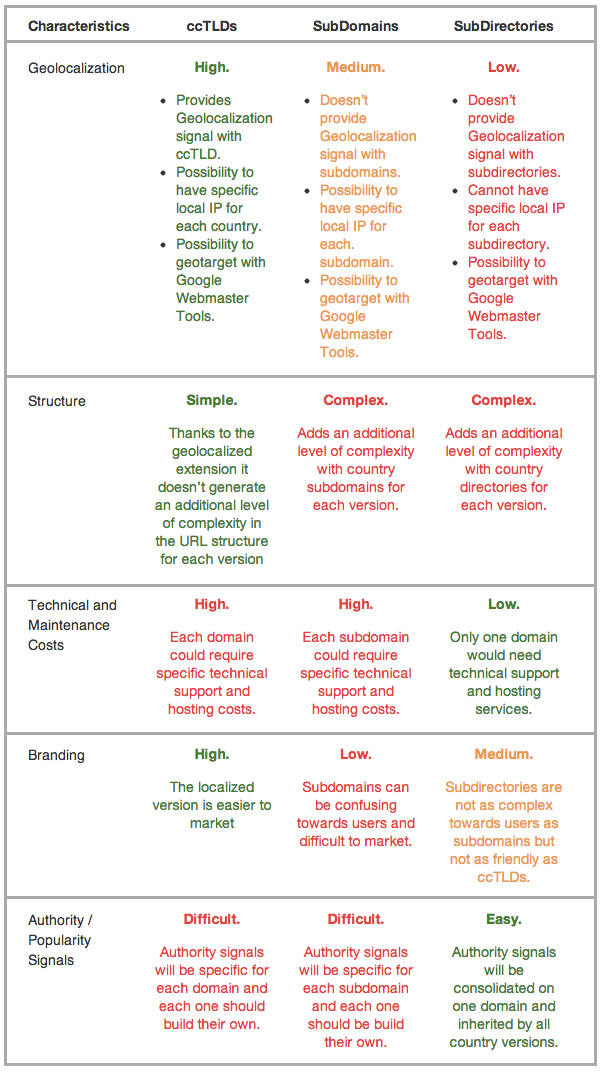
As you have seen, with all of the previous options of international organization structures, you will always have pros and cons and you will need to identify which is the best alternative for your own present and potentially future situation, depending on your own characteristics, strengths, resources and how you expect to grow in the future, to make sure it's a scalable configuration. Nonetheless, from my experience:
- For a language targeted site, if you don't have a high amount of technical resources to invest by managing different sub-domains, which will also end-up needing more maintenance and independent popularity signals, the most straight forward structure at the beginning is the sub-directories one.
- For a country targeted site, the ideal situation is to have a ccTLD –the one that offers more and better geolocalization signals, branding experience and less URL organization complexity-. Nonetheless it’s suitable if you have enough resources to maintain the related costs and build authority signals for each one of the country versions --ideally also having a local country IP--. This is usually the best for already well established sites that are looking to expand their business internationally. If this is not the case then starting with a sub-directory structure that will at some point be migrated to its specific ccTLD would be the alternative.
What you definitely want to avoid is having a "mixed" organization, which will be potentially more complex to manage and also confusing for users, for example using subdomains for both language and countries:
This is why it's so important to analyze and plan well from the start and assess all the different alternatives, to have a consistent organization that will work well not only at the start but also in the future.
4. Take the Content and Technical Resources into Consideration
The following step is to verify that you have the technical and content related resources to implement the best site structure according to your situation (using the criteria mentioned before).
As you can see your technical resources will be a very important factor to facilitate --or not-- the launching of a new language or country version of your site: Does it allow to set the previously described organization structures? Is it scalable?
More specifically, not only from a technical perspective but also from your content support capacity, you will need to verify you can configure and optimize the following aspects for the pages of your language or country versions: (1) unique titles and descriptions in the relevant language, effectively localized to the relevant geographic area, (2) localized contact and support information, (3) visible and crawlable currency and language switching options, (4) navigational elements in the relevant language, (5) localized headings in the relevant language, (6) localized information of the page in the relevant language, (7) reviews and comments in the relevant language, as it can be seen in the following image:
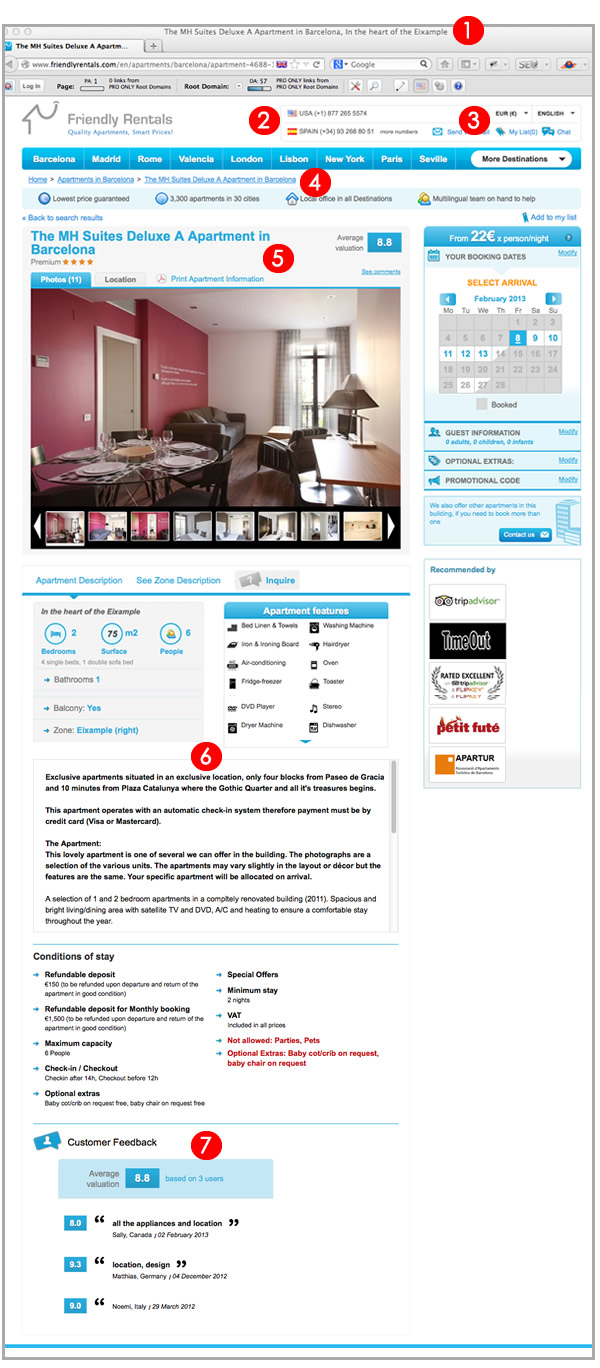
This might sound simple right? Sometimes it can be more complex than it seems because of the amount of content and pages. Always keep into consideration you will need to make sure to have not only the capacity to initially optimize but also support the language in a day-to-day basis, since you will need to verify the UGC, reply to your visitors questions, create assets and write a blog in the language to attract links and visibility, manage your international community in that language, do outreach to identify and create relationships with potential collaborators in your industry, etc.
As you can see even some big sites don't follow these good practices:
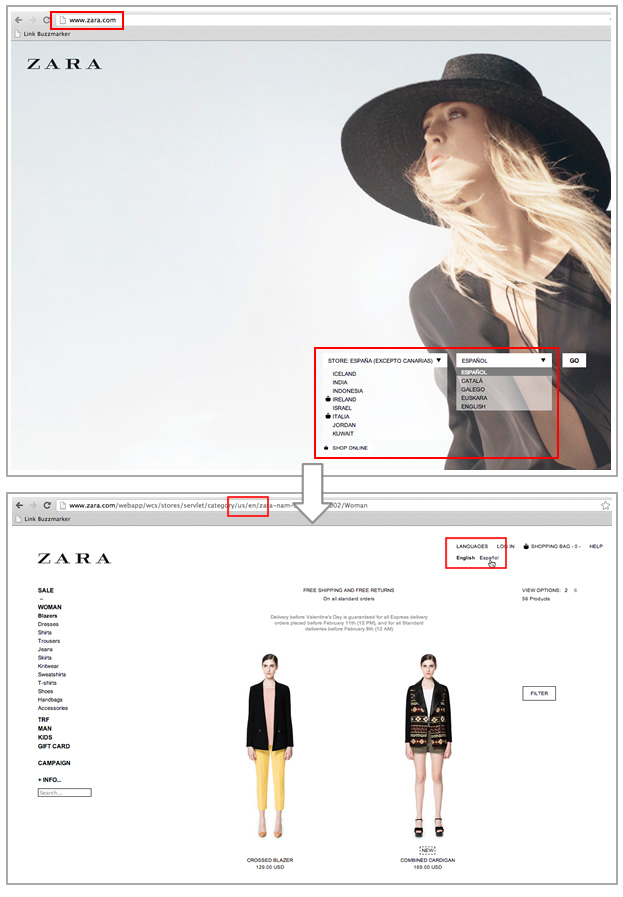
- Zara does not give the option to switch from one country to another (just language, usually English and the local one) once you have selected it on the home page and enter to the specific site:
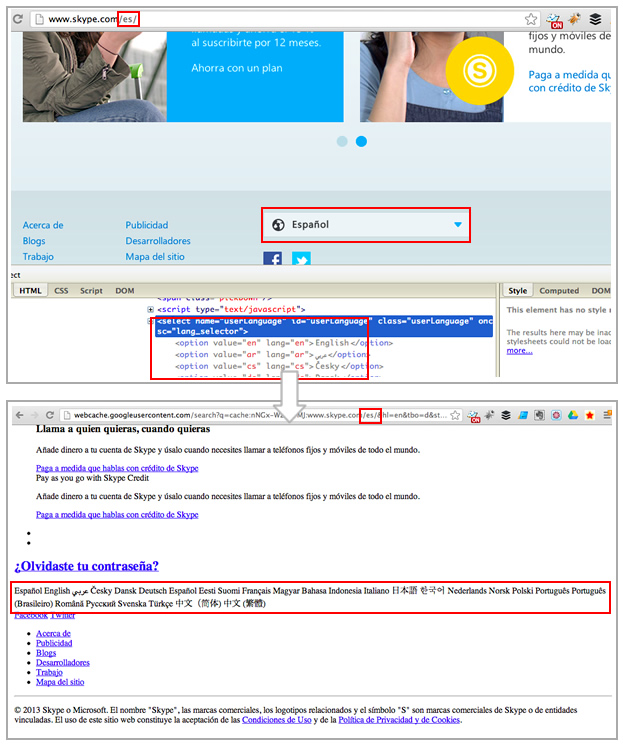
- Skype language menu is non-crawlable:
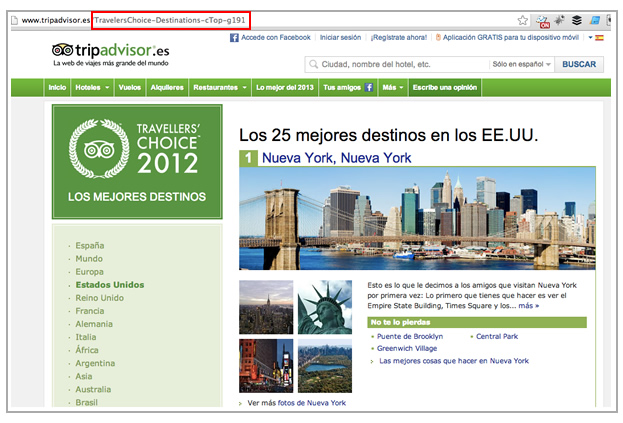
- Tripadvisor URLs are not in the relevant site version language:
5. Assessing and Planning your International Web Expansion
After having analyzed and identified all of the internal situation, external potential, besides the content, business and technically related aspects and and what you will need to have the best site structure in your situation, you will be able to assess: Will it be beneficial for your online business to expand with another language or country version? Will the related costs to have a new language or country versions covered by the potential organic traffic and conversions they will obtain?
If the numbers still don't convince you, you can also test the market and maintain the costs as low as possible at the beginning, by starting just with your most important product or service offerings for the language or country market with the highest potential -keeping the new site version structure small- and see if it has the traction and behavior you had identified for that area during your research and analysis, before launching a full site.
It's fundamental that you set specific SEO "SMART" Goals (related to your online business goals of course) for your new language or country versions. As you can see, although this analysis and assessing might take some time, by doing this you will make sure that your international SEO process is well structured and planned, with realistic goals and the most suitable structure in your case and will have much more chances to be successful.
In the next post I'm going to share how the best practices and consideration to take during the International SEO Process implementation. If you have any questions about this first phase of the process though, please leave a comment!
Image taken from Flickr under creative commons.